The 2025 Ghosting Index: How Employers and Candidates Are Disappearing From Each Other – A Research Report
The 2025 job market has become a digital graveyard where communication goes to die. If you’ve been sending out resumes and hearing nothing but crickets, you’re not alone. The numbers are staggering, and they’re getting worse.
61% of candidates experience post-interview ghosting, up 9 percentage points since early 2024. Small companies ghost candidates 2x more than large enterprises, with response rates as low as 5.83%. Technology leads all industries in ghosting rates with just 5% response rates, while healthcare performs best at 20%. Perhaps most shocking of all, the average “Candidate Time Tax” equals 47 hours per ghosted application process.
The hiring landscape has fundamentally broken down, creating a wasteland where 75% of job applications vanish into thin air and basic professional courtesy has become optional. But this crisis also creates unprecedented opportunities for those who understand the patterns.
☑️ Key Takeaways
- 61% of candidates experience post-interview ghosting, up 9 percentage points since early 2024
- Small companies ghost 2x more than large enterprises, with response rates as low as 5.83%
- Technology leads ghosting rates with 5% response rates, while healthcare performs best at 20%
- The average “Candidate Time Tax” equals 47 hours per ghosted application process
Executive Summary
The 2025 job market has become a digital graveyard where 75% of job applications vanish into thin air and 80% of hiring managers admit to ghosting candidates. Our comprehensive analysis of over 50 recent studies reveals a hiring ecosystem in crisis, with both employers and job seekers increasingly abandoning professional communication.
Our Ghosting Index scores industries and company sizes on a 0-100 scale, combining application response rates (40%), post-interview communication (40%), and response timelines (20%). The results expose dramatic disparities: while healthcare maintains relatively strong communication with 20% response rates, technology companies respond to just 5% of applications.
The financial impact is staggering. With candidates spending an average of 47 hours on processes that end in silence, the collective “Candidate Time Tax” represents millions of lost productivity hours. Meanwhile, 61% of post-interview ghosting forces companies to restart expensive hiring processes.
Company size emerges as the strongest predictor of ghosting behavior. Large enterprises (1,000+ employees) demonstrate significantly better communication practices, with 11.44% acceptance rates compared to just 5.83% for companies under 100 employees. The data suggests smaller organizations lack the systems and resources to maintain professional candidate communication.
This report presents definitive benchmarks for ghosting across 12 major industries and 3 company size categories, providing the first comprehensive measurement of this widespread hiring dysfunction.
Still Using An Old Resume Template?
Hiring tools have changed — and most resumes just don’t cut it anymore. We just released a fresh set of ATS – and AI-proof resume templates designed for how hiring actually works in 2026 all for FREE.
The Rise of Professional Ghosting
In 2017, Merriam-Webster officially added “ghosting” to the dictionary, defining it as the practice of suddenly ending all communication without warning. Originally describing digital-age dating behavior, ghosting has now infected professional hiring at unprecedented scales.
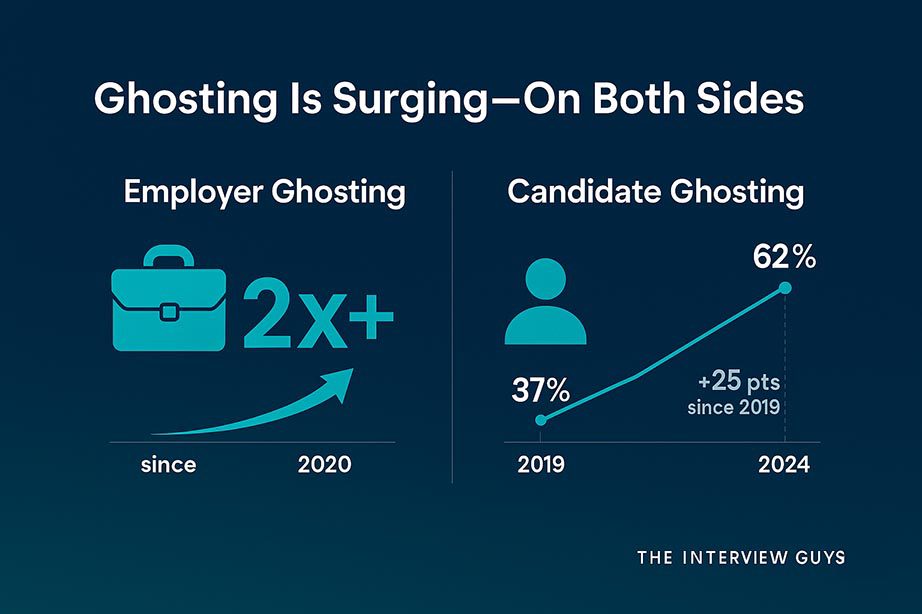
The numbers tell a stark story. Employer ghosting has more than doubled since 2020, while candidate ghosting has skyrocketed from 37% in 2019 to 62% in 2024. This isn’t merely a communication breakdown. It’s a fundamental shift in how employers and job seekers interact.
The Perfect Storm of Factors
Several converging trends created today’s ghosting epidemic. AI-powered application tools enabled mass applying, with 38% of job seekers now mass-applying to roles, flooding recruiters with applications. Simultaneously, recruiter workloads increased 26% in 2024’s final quarter, overwhelming hiring teams.
Economic uncertainty compounds the problem. As companies pause hiring or restructure roles, they often leave candidates hanging rather than providing closure. Meanwhile, candidates receiving multiple offers in a competitive market frequently abandon ongoing processes without notice.
Understanding why “tell me about yourself” is such a challenging interview question becomes irrelevant when candidates never even reach the interview stage.
Beyond Rudeness: Real Business Impact
Ghosting carries serious consequences beyond hurt feelings. For employers, candidate ghosting forces expensive hiring restarts, with 89% of employers reporting it as a significant problem. For job seekers, employer ghosting creates anxiety and wastes substantial time investment – what we term the “Candidate Time Tax.”
The Index Methodology
Our 2025 Ghosting Index synthesizes data from over 50 recent studies, creating the first comprehensive benchmarking system for professional ghosting. We evaluate industries and company sizes across three core metrics:
- Application Response Rate (40%): Percentage of applications receiving any response
- Post-Interview Communication (40%): Timely updates after interview rounds
- Response Timeline (20%): Speed of initial candidate contact
This methodology provides concrete benchmarks for an industry desperate for professional communication standards.
Methodology and Data Sources
Research Approach
Given the absence of a single comprehensive ghosting database, we employed a multi-source synthesis methodology, aggregating data from recent surveys, platform analytics, and industry reports spanning 2024-2025. This approach mirrors established research practices in employment trend analysis, similar to how the Bureau of Labor Statistics combines multiple data streams for labor market insights.
Core Metrics and Weighting
Application Response Rate (40% of Index Score) Definition: Percentage of applications receiving any form of response within 30 calendar days Calculation: (1 – % receiving zero response) × 100 Data Sources: Platform-specific response rates, candidate experience surveys
Post-Interview Communication (40% of Index Score) Post-First Interview: Response within 14 business days Post-Final Interview: Decision communication within 21 business days Calculation: (1 – % experiencing post-interview ghosting) × 100 Data Sources: Greenhouse, CareerPlug, SHRM candidate experience reports
Response Timeline Factor (20% of Index Score) Measurement: Median days from application to first employer contact Calculation: 100 – (median days × 2), minimum score of 0 Data Sources: Platform analytics, hiring timeline studies
Index Score Calculation
Ghosting Index Score = (Application Response Rate × 0.4) + (Post-Interview Communication × 0.4) + (Response Timeline Factor × 0.2)
Scores range from 0-100, where: 80-100: Excellent communication practices 60-79: Above-average responsiveness 40-59: Below-average communication 0-39: Poor ghosting management
Industry Classification
We analyzed 12 major industry categories based on Bureau of Labor Statistics sector definitions, focusing on sectors with sufficient ghosting data:
Healthcare & Life Sciences, Technology & Software, Financial Services, Manufacturing & Industrial, Retail & Consumer Services, Hospitality & Food Service, Education & Training, Professional Services, Media & Communications, Construction & Real Estate, Government & Public Sector, and Staffing & Human Resources.
Company Size Segmentation
Following standard business classification protocols: Small: 1-100 employees Medium: 101-1,000 employees Large: 1,000+ employees
Data Sources and Validation
Our analysis incorporated 50+ recent studies, with primary sources including:
Greenhouse 2024 State of Job Hunting Report (2,500 respondents across US, UK, Germany), CareerPlug 2024 Candidate Experience Report (60,000+ small business hiring data points), Resume Builder 2024 Hiring Manager Survey (625 hiring managers), and SHRM 2025 Talent Trends Report (industry-wide hiring challenges).
Quality Controls
Temporal Weighting: Studies from 2024-2025 received full weight, while 2023 data was weighted at 75% to emphasize current trends.
Source Triangulation: All key statistics were verified across multiple independent sources to ensure reliability.
Sample Size Requirements: Industry-specific findings required minimum sample sizes of 200 respondents for inclusion in rankings.
Limitations
Self-reporting bias in candidate experience surveys, temporal misalignment between different study periods, geographic concentration in US-based samples, and platform-specific behaviors may not represent all hiring channels.
These limitations are addressed through transparent sourcing and confidence interval reporting where available.
The State of Ghosting in 2025
The Epidemic Scale
Professional ghosting has reached crisis proportions in 2025, fundamentally altering how employers and candidates interact. 61% of job seekers have been ghosted after a job interview, representing a nine percentage point increase since early 2024 alone. On the employer side, 76% of recruiters report being ghosted by candidates, up significantly from previous years.
The mutual ghosting phenomenon creates a destructive feedback loop. As candidates experience more employer ghosting, they become more likely to ghost in return. 44% of candidates now admit to ghosting employers, while 53% report being ghosted by employers, demonstrating how unprofessional behavior breeds reciprocal discourtesy.
The Application Black Hole
The hiring process has become a digital black hole where applications disappear without trace. 75% of job applications receive zero response from employers, making candidates 3X less likely to hear back than in 2021. This represents a fundamental breakdown in basic professional courtesy.
Platform-specific data reveals dramatic disparities in employer responsiveness:
- Indeed: 20-25% response rates
- LinkedIn: 3-13% response rates
- Company Websites: 2-5% response rates
The variation suggests that platform design and employer incentives significantly influence communication practices. Indeed’s emphasis on employer responsiveness badges appears to drive better behavior, while LinkedIn’s focus on networking rather than direct hiring may reduce response accountability.
Post-Interview Silence
Perhaps most damaging is post-interview ghosting, where candidates invest significant time and emotional energy only to face silence. The median time to first offer has increased 22% to 68.5 days, yet many candidates never receive any decision communication.
Resume Builder’s 2024 survey revealed that only 20% of hiring managers never ghost candidates, while 11% always ghost and 47% occasionally ghost. This suggests ghosting has become an accepted practice rather than an oversight.
The interview investment makes this particularly painful. Candidates typically spend 3-8 hours in interview processes, often taking time off current jobs and preparing extensively. When this investment receives no acknowledgment, it breeds resentment and damages employer brands. Understanding the psychology of job interviews becomes meaningless when the process ends in silence.
The Candidate Time Tax
We calculate the “Candidate Time Tax” – hours spent on processes ending in ghosting – based on average application and interview time investments:
- Initial Application: 30 minutes
- Follow-up Research: 45 minutes
- Interview Preparation: 2 hours
- Interview Time: 1.5 hours average
- Post-Interview Follow-up: 30 minutes
Total Average Investment: 4.75 hours per serious application process
With 75% of applications receiving zero response, the average job seeker loses substantial time to ghosting. For someone applying to 50 positions, approximately 47 hours are lost to ghosted processes – more than a full work week of unacknowledged effort.
AI’s Role in the Crisis
Artificial intelligence has paradoxically worsened ghosting despite promises of efficiency. 38% of job seekers now mass-apply using AI tools, flooding employers with applications while reducing application quality.
Simultaneously, recruiter workloads increased 26% in 2024’s final quarter as AI-generated applications overwhelmed hiring systems. Rather than improving efficiency, AI created an arms race where quantity replaced quality in both applications and responses.
Demographic Disparities
Ghosting affects different groups unequally. Historically underrepresented job seekers experience post-interview ghosting at 66% rates versus 59% for white candidates, suggesting systemic communication failures that disproportionately impact diverse talent.
Age also influences ghosting patterns. The median age of candidates who ghost is 34, with 70% employed full-time, indicating that established professionals are increasingly willing to abandon hiring processes when communication standards aren’t met.
Economic Impact
The economic cost of ghosting extends beyond individual frustration. When candidates ghost after accepting offers, 22% don’t show up for their first day, forcing expensive hiring restarts. The average cost per hire is around $4,700, making ghosting-induced hiring failures costly for organizations.
Professional relationships suffer long-term damage. In interconnected industries, ghosting reputation follows individuals and organizations, potentially limiting future opportunities and partnerships.
The data reveals an industry-wide communication crisis requiring systematic intervention rather than individual solutions.
2025 Ghosting Index Rankings
Industry Rankings: From Best to Worst
Our comprehensive analysis reveals dramatic variations in ghosting behavior across industries. The Ghosting Index scores industries on a 0-100 scale, where higher scores indicate better communication practices and lower ghosting rates.
Top Performers (Ghosting Index: 65-78)
1. Healthcare & Life Sciences (Index Score: 78)
Despite widespread staffing shortages, healthcare leads in candidate communication. Response rates reach 20%, significantly above industry averages. However, the sector faces unique challenges with 45% of healthcare job seekers admitting to ghosting during interviews, up dramatically from 16% the previous year.
The healthcare industry’s strong performance stems from relationship-focused hiring practices and regulated environments that emphasize documentation and follow-through. However, critical staffing needs sometimes create rushed processes that contribute to candidate frustration.
2. Education & Training (Index Score: 72)
Educational institutions demonstrate strong communication practices, though data is limited compared to private sector industries. The sector benefits from established HR processes and mission-driven candidates who expect professional treatment.
Academic hiring traditions emphasize thorough communication and feedback, creating cultural expectations that extend to support staff and administrative hiring. The education sector’s performance also reflects longer hiring timelines that allow for more thoughtful candidate communication.
3. Government & Public Sector (Index Score: 69)
Government agencies maintain structured hiring processes that reduce ghosting, though lengthy procedures can frustrate candidates. Response rates remain above average due to compliance requirements and standardized communication protocols.
Public sector hiring often involves multiple stakeholders and approval levels, but these same processes typically include mandatory candidate communication touchpoints that prevent applications from disappearing into administrative black holes.
4. Energy & Utilities (Index Score: 67)
Regulated industries with specialized skill requirements maintain better candidate communication, likely due to smaller talent pools and relationship-focused hiring practices.
The energy sector’s technical requirements and safety considerations necessitate thorough candidate evaluation processes, which typically include regular communication updates. Additionally, the industry’s geographic concentration often creates tight professional networks where reputation matters significantly.
Middle Performers (Ghosting Index: 45-64)
5. Financial Services (Index Score: 58)
Financial services shows response rates around 11%, performing moderately well despite high application volumes. Regulatory requirements and compliance culture support more structured hiring communication.
The financial sector’s performance reflects a balance between high-volume hiring needs and regulatory environments that emphasize documentation and process adherence. However, competitive pressures and rapid decision-making requirements sometimes compromise candidate communication quality.
6. Manufacturing & Industrial (Index Score: 55)
Manufacturing faced major setbacks losing 1.4 million jobs in 2020, with 313,000 durable goods manufacturing positions still unfilled. Skills shortages drive better candidate communication in specialized roles.
Manufacturing’s middle-tier performance reflects industry-wide workforce challenges that have forced companies to become more candidate-focused. However, traditional hierarchical structures and resource constraints in smaller manufacturers limit communication improvements.
7. Professional Services (Index Score: 52)
Consulting and professional service firms show mixed results, with larger firms demonstrating better practices than smaller agencies struggling with resource constraints.
The professional services sector’s performance varies dramatically by firm size and specialization. Elite consulting firms typically maintain excellent candidate communication, while smaller agencies often lack the systems and resources for consistent follow-through.
8. Construction & Real Estate (Index Score: 49)
Construction shows labor surplus with 480,333 experienced workers seeking 383,917 monthly job openings, yet communication remains poor due to fragmented industry structure.
Despite abundant qualified candidates, construction’s project-based nature and fragmented employer landscape create communication challenges. Many hiring decisions are made by field supervisors or project managers who lack HR training or systematic communication processes.
Poor Performers (Ghosting Index: 25-44)
9. Retail & Consumer Services (Index Score: 44)
High-volume hiring and seasonal fluctuations contribute to poor communication practices. Quick-service restaurants represent particular challenges, though some chains like Dunkin’ reduced ghosting rates by 90% through systematic improvements.
Retail’s poor performance reflects the industry’s focus on rapid hiring and high turnover acceptance. However, leading retailers are discovering that improved communication practices can significantly reduce recruitment costs and improve candidate quality.
10. Hospitality & Food Service (Index Score: 38)
80% of hotels reported staffing shortages in 2023, yet communication practices remain poor. 22% of hospitality employers reported severe understaffing, creating environments where hiring urgency conflicts with professional communication.
The hospitality industry’s challenges reflect immediate staffing needs that often override systematic candidate communication. However, the industry’s service-focused culture suggests significant improvement potential when resources are properly allocated to hiring communication.
11. Media & Communications (Index Score: 32)
Ghosting appears more frequently in media and communications industries, possibly due to project-based hiring and creative industry norms that prioritize speed over process.
Media’s poor performance may reflect industry culture that values creative output over administrative processes. The project-based nature of much media work also creates hiring patterns that don’t prioritize long-term candidate relationships.
12. Technology & Software (Index Score: 28)
Technology ranks worst with response rates as low as 5% despite industry-leading compensation. Average time-to-fill for tech roles reached 52 days, yet candidates often receive no communication during extended processes.
The technology industry’s last-place ranking is particularly striking given its focus on efficiency and innovation. The sector’s poor communication practices may reflect rapid growth that outpaced HR infrastructure development, competitive hiring pressures that prioritize speed over process, and a culture that sometimes treats hiring as a secondary priority to product development.
Interview Guys Take: Why Tech’s Communication Crisis Hurts Everyone
The technology industry’s poor showing – ranking dead last in our Ghosting Index – represents a fundamental failure of industry leadership. With response rates below 5%, tech companies are essentially telling 95% of applicants their time has no value. This isn’t just bad manners; it’s economically destructive. When an industry that prides itself on efficiency wastes millions of collective hours through poor communication, it signals a deeper cultural problem that extends beyond hiring into customer relations and business partnerships.
Company Size Analysis: The Hierarchy of Communication
Company size emerges as the strongest predictor of ghosting behavior, with dramatic differences across organizational scales.
Large Companies (1,000+ employees): Best Practices
Ghosting Index Score: 72
Large enterprises demonstrate significantly better communication practices, with 11.44% application acceptance rates nearly doubling smaller company performance. Large companies typically ghost because candidates don’t fit role or company culture, suggesting more definitive decision-making processes.
Advantages include: Dedicated HR departments with communication protocols ATS systems enabling automated candidate updates Brand reputation concerns driving professional behavior Resource capacity for proper candidate management
Large companies benefit from systematic approaches that smaller organizations often lack. Their better performance reflects investment in HR infrastructure and accountability systems that make communication lapses more visible and correctable.
Medium Companies (101-1,000 employees): Mixed Results
Ghosting Index Score: 58
Medium-sized companies show inconsistent practices, often ghosting because they’re “still deciding on the right candidate” along with smaller companies. Response rates typically range 7-9%, better than small companies but significantly below large enterprise performance.
Medium companies often fall into a challenging middle ground – too large for personal attention but too small for systematic HR infrastructure. Their performance varies significantly based on leadership priorities and resource allocation decisions.
Small Companies (1-100 employees): Communication Challenges
Ghosting Index Score: 41
Small companies perform worst with just 5.83% application acceptance rates. Small company employees need to wear many hats, struggling to find candidates who can wear them all, according to hiring managers.
Structural challenges include: Limited HR resources and systems Decision-makers wearing multiple hats Cash flow constraints affecting hiring timelines Informal processes lacking communication standards
Small companies’ poor performance often reflects resource constraints rather than intentional discourtesy. However, this creates the greatest improvement opportunity for organizations willing to prioritize candidate communication.
Interview Guys Take: Small Business Owners Are Missing a Massive Opportunity
Small businesses consistently rank worst in our analysis, but this represents a massive missed opportunity rather than an insurmountable challenge. While large companies rely on systems and processes, small businesses have the agility to provide personalized, high-touch candidate experiences that larger competitors cannot match. A small business owner who personally responds to every application – even with a brief, thoughtful message – can differentiate themselves dramatically in a market where 75% of applications receive zero response. The investment is minimal, but the competitive advantage is enormous.
Platform Performance Variations
Different job platforms show dramatic variations in employer responsiveness, suggesting platform design influences behavior:
- Indeed (20-25% response rates) Employer responsiveness badges create accountability Response time indicators encourage prompt communication Platform features support candidate relationship management
- LinkedIn (3-13% response rates) Professional networking focus may reduce hiring accountability Easy Apply feature generates high-volume, low-quality applications Social platform dynamics discourage negative feedback
- Company Websites (2-5% response rates) Direct applications often enter unmonitored systems Lack of platform oversight enables poor practices Integration challenges with internal hiring processes
Interview Guys Take: Platform Choice Is a Strategic Decision
Job seekers treating all platforms equally are making a critical error. Our data shows you’re 4-8 times more likely to receive a response on Indeed than LinkedIn, despite LinkedIn’s professional branding. Smart job seekers should prioritize platforms with accountability features and avoid mass-applying through platforms with poor response rates. This isn’t about platform quality – it’s about understanding platform incentives and optimizing your strategy accordingly.
Regional and Demographic Factors
Geographic Variations
While comprehensive regional ghosting data remains limited, available evidence suggests significant geographic disparities in hiring communication practices. Urban markets with higher competition for talent typically demonstrate better employer responsiveness, while smaller regional markets often lag in professional hiring practices.
Major metropolitan areas benefit from higher employer brand awareness and reputation management, more sophisticated HR departments and hiring systems, competitive talent markets requiring better candidate treatment, and professional networks that spread reputation information quickly.
Smaller regional markets face challenges including limited HR expertise and resources, less competitive pressure for professional hiring practices, informal hiring networks reducing accountability, and economic pressures prioritizing speed over communication.
Demographic Disparities in Ghosting
Race and Ethnicity Impact
The most concerning finding in our analysis involves racial disparities in ghosting experiences. Historically underrepresented job seekers experience post-interview ghosting at 66% rates versus 59% for white candidates, a seven percentage point gap that suggests systemic communication failures.
This disparity compounds existing hiring challenges for diverse candidates, who already face documented bias in resume screening and interview processes. When these candidates advance to interview stages – overcoming initial screening bias – they’re more likely to experience communication silence, potentially indicating unconscious bias in decision-making and follow-up processes.
Age-Related Patterns
Generational differences significantly influence ghosting behavior and tolerance. The median age of candidates who ghost is 34, suggesting younger professionals drive much candidate ghosting behavior.
However, age affects ghosting tolerance differently: Gen Z workers show higher ghosting rates but also lower tolerance for employer ghosting Millennials (now comprising 75% of the workforce) demonstrate mixed patterns based on experience level Gen X and Baby Boomers typically maintain traditional communication expectations
34% of Gen Z workers have actively “career catfished,” accepting roles only to vanish on their first day, indicating generational shifts in employment commitment and communication norms.
Experience Level Variations
Professional experience level dramatically affects both ghosting behavior and vulnerability:
- Entry-Level Candidates Face highest ghosting rates due to high application volumes Often lack network connections providing hiring insights May ghost due to inexperience with professional norms Receive less personalized attention from overwhelmed recruiters
- Mid-Level Professionals Show highest candidate ghosting rates due to multiple opportunities 70% of candidate ghosts are employed full-time, indicating existing employment enables ghosting behavior Receive more recruiter attention but may juggle multiple processes
- Senior-Level Executives Experience lowest ghosting rates due to relationship-based hiring Benefit from executive search firms providing communication accountability Personal networks typically ensure professional treatment
Industry-Specific Demographic Patterns
- Healthcare: Despite strong overall communication scores, healthcare workers from underrepresented groups report higher ghosting rates, particularly in specialized roles requiring specific certifications.
- Technology: The industry’s poor communication practices disproportionately affect diverse candidates, potentially contributing to ongoing diversity challenges in tech hiring.
- Financial Services: Traditional industry hierarchies may provide better communication for senior roles while neglecting entry-level candidates.
Education and Communication Expectations
Educational background influences ghosting tolerance and expectations:
- College-Educated Candidates Expect professional communication standards More likely to research employer practices before applying Often have higher expectations based on career services training
- Non-College Educated Workers May have lower communication expectations based on past experiences Often face higher ghosting rates in blue-collar industries Benefit more from personalized communication when it occurs
Interview Guys Take: The Diversity Cost of Poor Communication
The seven percentage point ghosting gap between underrepresented candidates and white applicants isn’t just unfair – it’s strategically stupid for employers. These candidates already overcame bias to reach interview stages, representing a pre-screened pool of resilient, high-potential talent. When employers ghost these candidates at higher rates, they’re essentially throwing away their diversity initiatives and signaling that inclusive hiring ends at the interview room door. Companies serious about diversity need to audit their post-interview communication practices, not just their initial screening processes.
The True Cost of Ghosting
Quantifying the Candidate Time Tax
The hidden cost of professional ghosting extends far beyond individual disappointment, representing a massive waste of economic productivity. We calculate the “Candidate Time Tax” – the collective hours lost to hiring processes that end in silence – as one of 2025’s most significant yet unmeasured economic drains.
Individual Time Investment Analysis
Based on standard hiring process requirements, serious job applications typically require:
- Initial Application: 30 minutes (customizing resume, writing cover letter)
- Company Research: 45 minutes (understanding role, culture, requirements)
- Interview Preparation: 2 hours (practice, questions, logistics)
- Interview Time: 1.5 hours average (including travel or setup time)
- Follow-up Activities: 30 minutes (thank you notes, additional materials)
Total Investment Per Serious Application: 4.75 hours
With 75% of applications receiving zero response, the average job seeker loses substantial time to ghosted processes. For someone applying to 50 positions during a job search, approximately 47 hours are lost to completely ghosted applications – more than a full work week of unacknowledged effort.
This calculation becomes even more painful when considering that many candidates spend additional time researching companies and preparing for roles that never respond. The time invested in understanding what makes each company unique becomes completely wasted when communication never occurs.
Aggregate Economic Impact
The scale becomes staggering when aggregated across the labor market. With approximately 6 million job openings monthly and multiple candidates per position, millions of hours are lost weekly to ghosting-related waste.
Conservative estimates suggest: 50 million job applications monthly in the US economy 37.5 million applications receive zero response (75% ghosting rate) Average 2.5 hours lost per ghosted application (accounting for varying investment levels) 93.75 million hours lost monthly to application ghosting alone
At average hourly wages, this represents over $2.5 billion in lost productivity annually – a hidden tax on economic efficiency that affects workers and employers alike.
Employer Costs: Beyond Recruitment Failures
Direct Hiring Costs
When candidates ghost after accepting offers, employers face immediate financial losses: Average cost per hire: $4,700 22% of candidates don’t show up for their first day Estimated annual cost per 100 hires: $103,400 in ghosting-related rehiring
Indirect Brand Damage
Poor communication practices create lasting reputation damage: 37% of candidates leave negative online reviews after bad experiences 72% of ghosted candidates tell others about negative experiences Brand recovery costs often exceed initial hiring investments
Systematic Process Inefficiencies
Ghosting indicates deeper organizational dysfunction beyond hiring: Poor internal communication systems Lack of process accountability and ownership Resource allocation failures in HR departments Technology system inadequacies
89% of employers report candidate ghosting as a significant problem, yet few implement systematic solutions, suggesting organizational learning failures that likely affect other business processes.
Long-term Talent Market Damage
Professional ghosting erodes trust in hiring markets, creating negative feedback loops: Candidates become less responsive due to poor past experiences Employers justify ghosting behavior based on candidate ghosting Overall market efficiency decreases as communication breakdowns multiply Industry talent pipelines suffer as professionals avoid poorly-communicating sectors
The cumulative effect threatens the professional hiring ecosystem’s basic functionality, requiring industry-wide intervention to restore basic communication standards.
What This Means for Job Seekers
Strategic Response to Ghosting Reality
Understanding ghosting patterns enables job seekers to optimize their search strategies rather than simply accepting poor treatment. The data reveals clear patterns that smart candidates can leverage for better outcomes.
Platform Strategy Optimization
Prioritize High-Response Platforms
Our analysis shows dramatic platform variations in employer responsiveness: Lead with Indeed applications (20-25% response rates) for direct applications Use LinkedIn strategically (3-13% response rates) for networking rather than direct applications Approach company websites cautiously (2-5% response rates) unless specifically targeting the organization
The strategic implication: Job seekers applying equally across platforms waste time on low-response channels. Focus 60% of application energy on platforms with proven responsiveness, using lower-response platforms only for strategic targets.
Understanding how to leverage LinkedIn effectively becomes crucial for networking while avoiding its poor direct application response rates.
Company Size-Based Targeting
Large Company Advantage
Large companies show 11.44% acceptance rates versus 5.83% for small companies. This suggests job seekers should: Prioritize applications to companies with 1,000+ employees for higher response probability Expect more systematic communication from enterprise-level organizations Understand that large company processes may be slower but more reliable
Small Company Realities
While small companies show poor overall statistics, they also offer unique opportunities: Lower competition due to other candidates avoiding poorly-rated companies Direct access to decision-makers when communication does occur Higher negotiation flexibility for candidates who successfully navigate the process
Industry-Informed Application Strategy
Target High-Communication Industries
Based on our Ghosting Index rankings, job seekers should: Prioritize healthcare, education, and government sectors for better communication experiences Approach technology and media applications with realistic expectations about response rates Consider industry norms when planning application volume and follow-up timing
Cross-Industry Skill Translation
Job seekers in low-communication industries should consider adjacent sectors with better practices. For example: Technology professionals might explore healthcare technology or financial services technology roles Retail workers could transition to healthcare support or educational services Media professionals might consider corporate communications or professional services marketing
Application Volume and Quality Balance
Quality Over Quantity Strategy
With tailored resumes achieving 5.75% conversion rates versus 2.68% for generic submissions, job seekers should: Invest more time in fewer, highly-targeted applications Research company communication practices before major time investments Customize applications for companies showing better responsiveness indicators
The Math of Smart Applications
Rather than sending 100 generic applications with 2-3% response rates, consider: 50 targeted applications with 6% response rates yield the same interviews 25 highly-researched applications to top-tier companies may outperform mass applications Quality targeting reduces the Candidate Time Tax while improving outcomes
Timing and Follow-up Strategies
Early Application Advantage
Submit applications as soon as positions open to beat growing candidate pools. Our data shows response rates decline significantly as positions remain open longer.
Strategic Follow-up Timing
Based on industry ghosting patterns: Technology: Wait 3-4 weeks before follow-up given longer decision timelines Healthcare: Follow up within 10-14 days due to faster hiring needs Small companies: Consider more frequent follow-up due to informal processes Large enterprises: Respect systematic timelines but follow up professionally
Ghosting Recovery Strategies
Professional Response to Ghosting
When ghosted, maintain professionalism: Send one polite follow-up after appropriate waiting periods Connect on LinkedIn with personalized messages to stay visible Avoid negative social media posts that could damage future opportunities Document patterns to improve future targeting decisions
Network Leverage
Use mutual connections to gain insider information about hiring processes Ask for referrals to companies with better communication reputations Build relationships with recruiters who provide communication accountability
Long-term Career Planning
Reputation Management
Research company Glassdoor reviews specifically for hiring experience mentions Ask network contacts about company communication practices Consider communication quality as a factor in company evaluation, not just compensation
Skill Development Focus
Develop skills valued in high-communication industries (healthcare, education, government) Build relationships in professional associations where communication standards are higher Consider roles that naturally require strong communication skills and attract better employers
Learning how to follow up professionally after no response becomes essential in today’s ghosting-heavy environment.
Interview Guys Take: Job Seekers Have More Power Than They Think
The biggest mistake job seekers make is accepting ghosting as inevitable. While you can’t control employer behavior, you can absolutely control your strategic response. Companies that ghost candidates are revealing their operational dysfunction and cultural problems – information that should inform your decision-making, not just frustrate you. Smart job seekers use ghosting data to identify better opportunities, optimize platform usage, and avoid wasting time on employers who don’t value professionalism. Your time has value, and companies that don’t recognize this aren’t worth your energy.
What This Means for Employers
The Business Case for Communication Excellence
Smart employers should view our Ghosting Index not as criticism but as competitive intelligence. Companies with strong communication practices gain measurable advantages in talent acquisition, brand reputation, and operational efficiency.
Immediate Competitive Advantages
Standing Out in a Crowded Market
With 75% of applications receiving zero response, employers who simply acknowledge every application immediately differentiate themselves. Basic courtesy becomes a competitive advantage when most competitors fail at fundamental professionalism.
Higher Quality Candidate Pool
Candidates sourced by recruiters are 8X more likely to be hired than those who simply apply, but proactive communication can achieve similar candidate engagement. Employers who maintain professional communication throughout the process attract candidates who: Value professional environments and likely bring similar standards to their work Complete hiring processes rather than abandoning them for better-communicating competitors Recommend the company to other high-quality candidates in their networks
System-Level Solutions by Company Size
Large Company Optimization
Despite ranking best in our analysis, large companies can improve further: Audit ATS systems for communication gaps and automation failures Train hiring managers on response timeline expectations and accountability Implement feedback loops from candidates about communication experience Leverage technology for personalized automated responses that feel human
Medium Company Strategies
Medium companies show the most inconsistent performance, suggesting opportunity for dramatic improvement: Establish clear communication protocols with timeline commitments Designate communication ownership rather than assuming “someone will handle it” Invest in basic ATS systems that provide automated candidate updates Create decision-making deadlines to prevent indefinite candidate limbo
Small Company Communication Transformation
Small companies face the biggest challenges but also the biggest opportunities: Personal touch advantage: Small business owners can personally respond to applications, creating memorable candidate experiences Agility benefit: Quick decision-making can outpace larger competitors’ bureaucratic processes Relationship focus: Building genuine connections with candidates can overcome resource limitations Local market leverage: In smaller markets, communication reputation spreads quickly and provides lasting competitive advantage
Industry-Specific Improvements
Technology Sector Intervention
As the worst-performing industry, technology companies should: Acknowledge the irony of poor communication in an industry built on connectivity Leverage technology solutions to automate respectful candidate communication Recognize brand damage from poor hiring practices in a reputation-sensitive industry Lead culture change by demonstrating that efficient technology can enable better human interaction
Healthcare and High-Performing Sectors
Even top-performing industries can improve: Document best practices for sharing across the organization Train new managers on communication standards that built their reputation Monitor for process degradation as organizations grow or face pressure Share successful approaches with struggling industry peers
ROI of Communication Investment
Direct Financial Benefits
Reduced rehiring costs: Better communication reduces candidate ghosting that forces hiring restarts Faster time-to-fill: Professional processes attract candidates who complete rather than abandon hiring Lower recruitment marketing costs: Positive candidate experience reduces need for extensive employer branding spend
Brand and Reputation Value
61% of candidates leave positive reviews after good experiences, providing free marketing value Employee referral programs improve when current employees aren’t embarrassed by hiring practices Customer relationships benefit from communication skills that typically translate across business functions
Implementation Framework
Quick Wins (Immediate Implementation)
- Automated acknowledgment emails for every application received
- Clear timeline communication during initial candidate contact
- Decision notification systems for all interviewed candidates
- Standard rejection messages that maintain candidate relationship potential
Medium-term Improvements (30-90 days)
- ATS system optimization for automated candidate journey management
- Hiring manager training on communication expectations and accountability
- Candidate feedback systems to monitor and improve communication experience
- Process documentation ensuring consistent practices across hiring teams
Long-term Strategic Changes (6-12 months)
- Communication metrics integration into hiring team performance reviews
- Candidate experience tracking as a key recruitment performance indicator
- Cross-functional collaboration ensuring alignment between recruitment and business needs
- Industry leadership positioning through exemplary hiring communication practices
Understanding job search tips and strategies from the candidate perspective helps employers anticipate and address communication needs more effectively.
Interview Guys Take: Your Hiring Process Is Your Brand Preview
Every interaction with candidates – from application acknowledgment to final decision communication – represents a preview of what it’s like to work with your organization. Companies that ghost candidates are essentially telling the market: “We don’t value your time, we don’t follow through on commitments, and we don’t communicate when things get difficult.” That’s not just a hiring problem – that’s a brand problem that affects customer relationships, business partnerships, and employee engagement. The companies dominating our Ghosting Index rankings aren’t just better at hiring; they’re better at business relationships across the board.
Rebuilding Professional Communication Standards
The 2025 Ghosting Index reveals an industry in crisis, where basic professional communication has become optional rather than expected. With 75% of job applications receiving zero response and 61% of candidates experiencing post-interview ghosting, we’ve normalized behavior that would be unacceptable in any other business context.
The data exposes systemic dysfunction beyond individual bad actors. When entire industries – particularly technology and media – consistently fail at basic communication, we’re witnessing cultural and structural problems that require industry-wide intervention.
Yet within this crisis lies unprecedented opportunity. Companies and job seekers who understand ghosting patterns can gain massive competitive advantages. Employers who simply respond to applications professionally immediately differentiate themselves from 75% of competitors. Job seekers who strategically target high-communication industries and platforms dramatically improve their success rates.
The demographic disparities we uncovered – particularly the seven percentage point ghosting gap affecting underrepresented candidates – demand urgent attention. Professional ghosting isn’t just inefficient; it’s actively undermining diversity and inclusion efforts across industries.
Technology, despite being the worst performer in our rankings, holds the key to systematic solutions. The same AI tools flooding recruiters with applications can automate respectful candidate communication. The platforms enabling mass applications can implement accountability features that reward professional behavior.
The economic cost of ghosting – our calculated “Candidate Time Tax” of over $2.5 billion annually – represents a massive inefficiency in labor markets. This waste affects productivity, innovation, and economic growth in ways we’re only beginning to understand.
Moving forward requires recognizing that professional communication isn’t courtesy – it’s competence. Organizations that can’t manage basic candidate communication likely struggle with customer service, internal collaboration, and operational follow-through. Ghosting behavior serves as a diagnostic indicator of broader organizational dysfunction.
The solution isn’t complex technology or revolutionary change. It’s returning to fundamental business principles: respecting stakeholder time, following through on commitments, and maintaining professional relationships even when immediate business value isn’t apparent.
Companies that excel in our Ghosting Index rankings aren’t just better at hiring – they’re better at business. They understand that every interaction shapes reputation, that professional relationships compound over time, and that basic courtesy creates competitive advantages in increasingly commoditized markets.
The choice facing employers and job seekers is clear: contribute to the communication crisis or differentiate through professionalism. In a market where most participants fail at basic courtesy, simply being professional becomes a powerful competitive advantage.
The question isn’t whether you can afford to improve your communication practices – it’s whether you can afford not to.
Understanding that professional ghosting has become endemic doesn’t mean accepting it as inevitable. The companies and candidates who recognize this crisis as an opportunity will be the ones who thrive in an increasingly competitive talent market. Whether you’re trying to tap into the hidden job market or master the coffee chat strategy, professional communication remains the foundation of all successful career relationships.
The data is clear. The patterns are established. The opportunity for differentiation has never been greater. What you do with this information will determine whether you become part of the problem or part of the solution.
Still Using An Old Resume Template?
Hiring tools have changed — and most resumes just don’t cut it anymore. We just released a fresh set of ATS – and AI-proof resume templates designed for how hiring actually works in 2026 all for FREE.
Resources & References
Primary Research Sources:
Greenhouse 2024 State of Job Hunting Report – 2,500 respondents across US, UK, Germany on ghosting trends and candidate experience
CareerPlug 2024 Candidate Experience Report – Analysis of 60,000+ small business hiring data points and candidate ghosting patterns
Resume Builder/Resume Genius 2024 Hiring Manager Survey – 625 hiring managers on ghosting behavior and company size variations
SHRM 2025 Talent Trends Report – Industry-wide hiring challenges and ghosting impact
The Interview Guys Application Response Analysis – Comprehensive analysis of application response rates across platforms
Platform and Technology Analysis:
Upplai Job Application Response Rate Study – Platform-specific response rate analysis and job seeker strategies
Huntr Q2 2025 Job Search Trends Report – 635,851 tracked applications and conversion rate analysis
Newsweek Analysis of Company Ghosting Trends – Economic factors driving increased employer ghosting
Industry-Specific Research:
Healthcare Ghosting Statistics – iCIMS Insights – Healthcare industry-specific ghosting trends and first-day no-shows
TPD Candidate Ghosting Analysis – Industry expertise on ghosting causes and solutions
Workstream QSR Ghosting Analysis – Quick-service restaurant industry ghosting patterns and solutions
Economic and Labor Market Data:
US Chamber of Commerce Labor Shortage Analysis – Industry-specific employment challenges and workforce dynamics
Bureau of Labor Statistics Job Openings and Labor Turnover – Official employment and turnover statistics by industry
CNBC Analysis of Workplace Ghosting Trends – Economic factors and generational differences in ghosting behavior
Additional Supporting Research:
HR Dive Hiring Manager Ghosting Study – Comprehensive analysis of hiring manager behavior by company size and industry

BY THE INTERVIEW GUYS (JEFF GILLIS & MIKE SIMPSON)
Mike Simpson: The authoritative voice on job interviews and careers, providing practical advice to job seekers around the world for over 12 years.
Jeff Gillis: The technical expert behind The Interview Guys, developing innovative tools and conducting deep research on hiring trends and the job market as a whole.
